Algorithms
Below is a series of different programs that have pseudocode and flowcharts completed for them. Use them to try and relate your algorithm designs to your code.
Click here to view the pseudocode code guide.
Click here to view the different flowchart symbols.
Example 1 - Teddy Bears Program - Sequencing
Python
hours = int(input("Enter the number of hours worked: "))
bears = int(input("Enter the number of teddy bears made: "))
hourswage = hours * 7
bearswage = bears * 0.45
total = hourswage + bearswage
print("Your total wage is: £{:.2f}".format(total))
Pseudocode |
Flowchart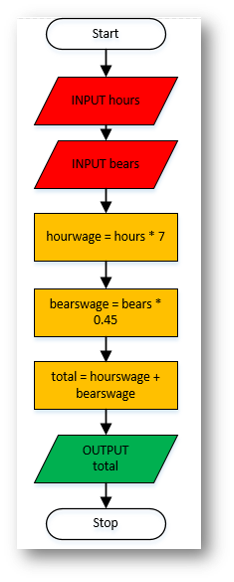 |
Example 2 - Water Temperature Program - Selection
Python
fahrenheit = float(input("Enter the temperature of the water in fahrenheit: "))
centigrade = (fahrenheit – 32) * (5/9)
if centigrade <= 0:
print("Water Frozen")
elif centigrade >=100:
print("Water Boiling")
else:
print("Water is neither frozen or boiling")
Pseudocode |
Flowchart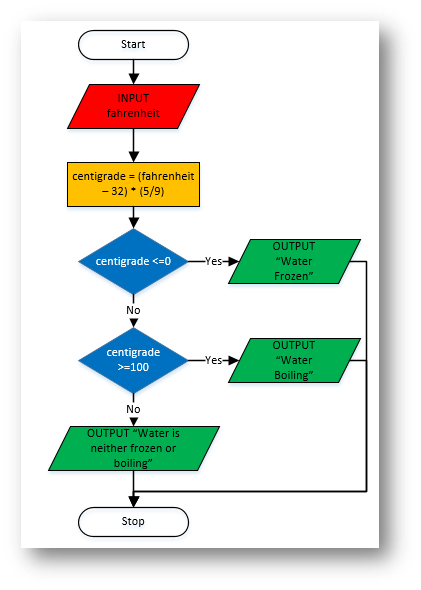 |
Example 3 - Average Calculator - Iteration (FOR)
Python
total = 0
numbers = int(input("How many numbers do you want to enter? "))
for x in range(numbers):
latest = int(input("Enter a number: "))
total = total + latest
average = total / numbers
print("The total of the numbers was " + str(total))
print("The average of the numbers was " + str(average))
Pseudocode | |
Flowchart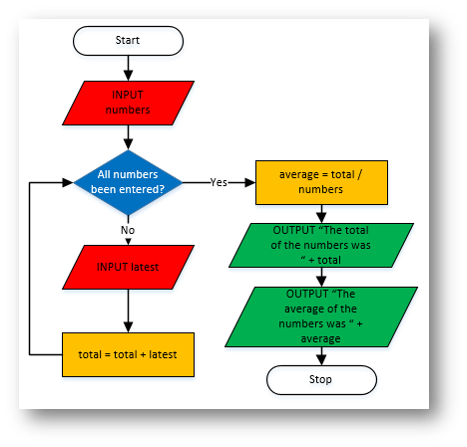 |
|
Example 4 - Menu Selection - Iteration (WHILE)
Python
print("What would you like to do?")
print("1. Play Game")
print("2. Instructions")
print("3. Quit")
valid = False
while valid==False:
option = int(input("Enter which option you want: "))
if option == 1 or option == 2 or option == 3:
valid=True
print("Let's go")
Pseudocode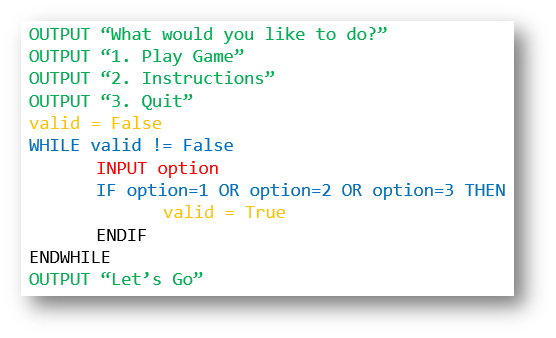 |
Flowchart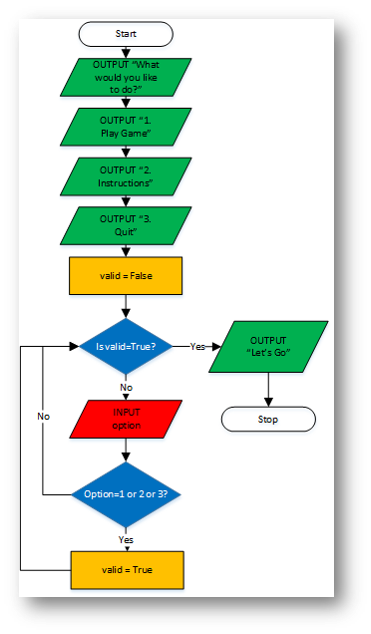 |
Example 5 - Login System - Reading from a File
Python
username = input("Please enter your username (email address): ")
password = input("Please enter your password: ")
file=open("Logins.csv","r")
found = False
for line in file:
details=line.split(",")
if details[0] == username and details[1] == password:
found = True
print("Email: " + details[0])
print("Name: " + details[2] + " " + details[3])
print("Address:\n" +details[4] +"\n"+details[5]+"\n"+details[6])
if found == False:
print("Incorrect login details entered")
Pseudocode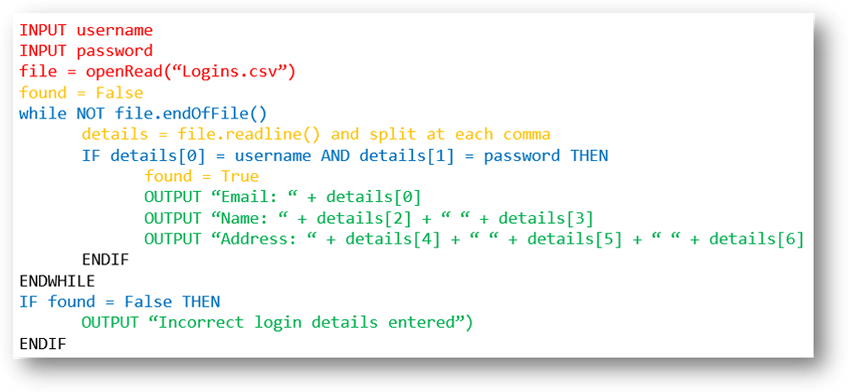 | |
Flowchart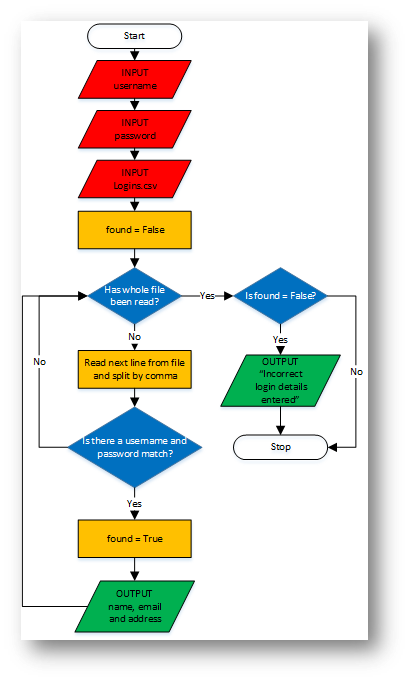 |
|
Example 6 - Product Catalogue - Writing to a File
Python
another = "Y"
while another == "Y":
barcode = input("Enter an 8 digit barcode: ")
description = input("Enter a product description: ")
price = input("Enter a price: ")
file=open("Products.csv","a")
file.write(barcode + "," + description + "," + price)
file.close()
print("Product added to catalogue")
another = input("Do you want to add another? Y/N ")
Pseudocode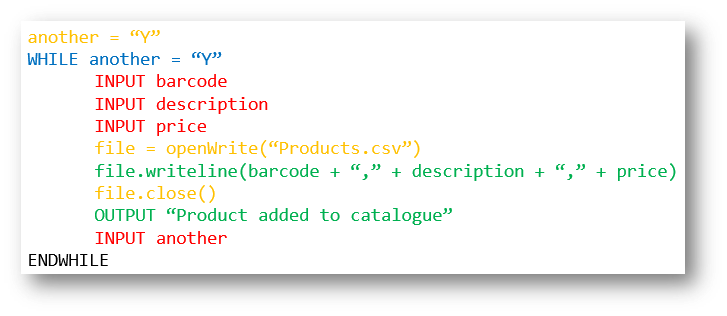 | |
Flowchart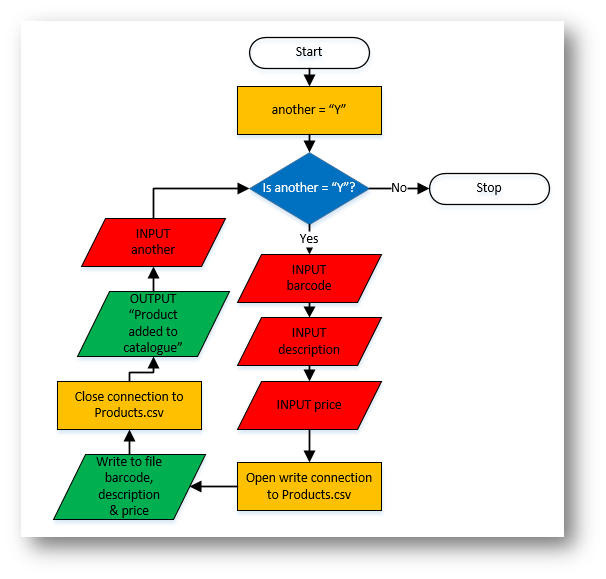 |
|
Example 7 - Measurement Conversion - Functions
Python
def mtokm(value):
answer = value*1.6
return answer
def kmtom(value):
answer = value*0.62
return answer
print("What conversion would you like to do?")
print("1. Convert Miles to Kilometres")
print("2. Convert Kilometres to Miles")
option = input(">>")
print()
number = float(input("Enter your measurement to convert: "))
if option=="1":
print(str(number) + " miles in KM is " + str(mtokm(number)))
elif option=="2":
print(str(number) + " KM in miles is " + str(kmtom(number)))
else:
print("Please enter a valid selection")
Pseudocode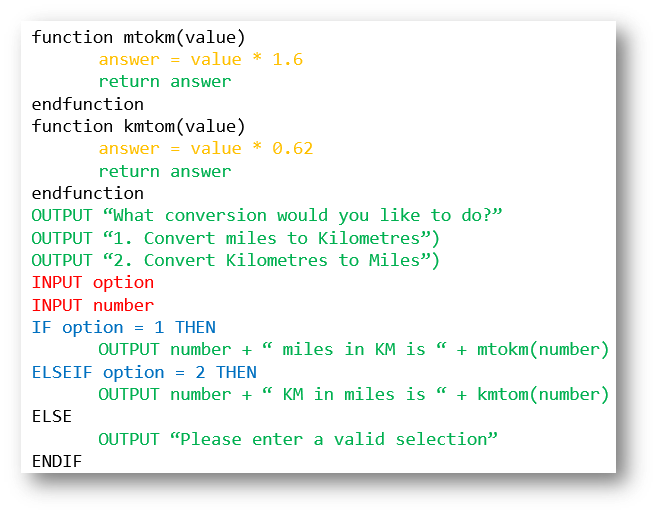 | |
Flowchart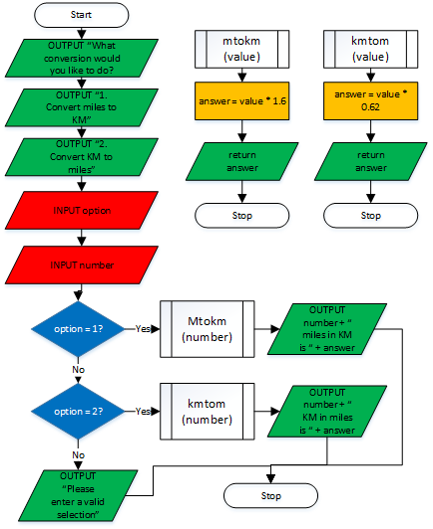 |
|